
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in a case of severe classic maple syrup urine disease. Management involves dietary changes, such as life-long dietary intake restriction of foods with branched-chain amino acids (especially leucine), and early treatment of metabolic decompensation, with agents such as intravenous glucose 9.

MRI brain may show the characteristic pattern of edema present in MSUD. There is elevated plasma concentrations of branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine), allo-isoleucine, and alpha-ketoacids.

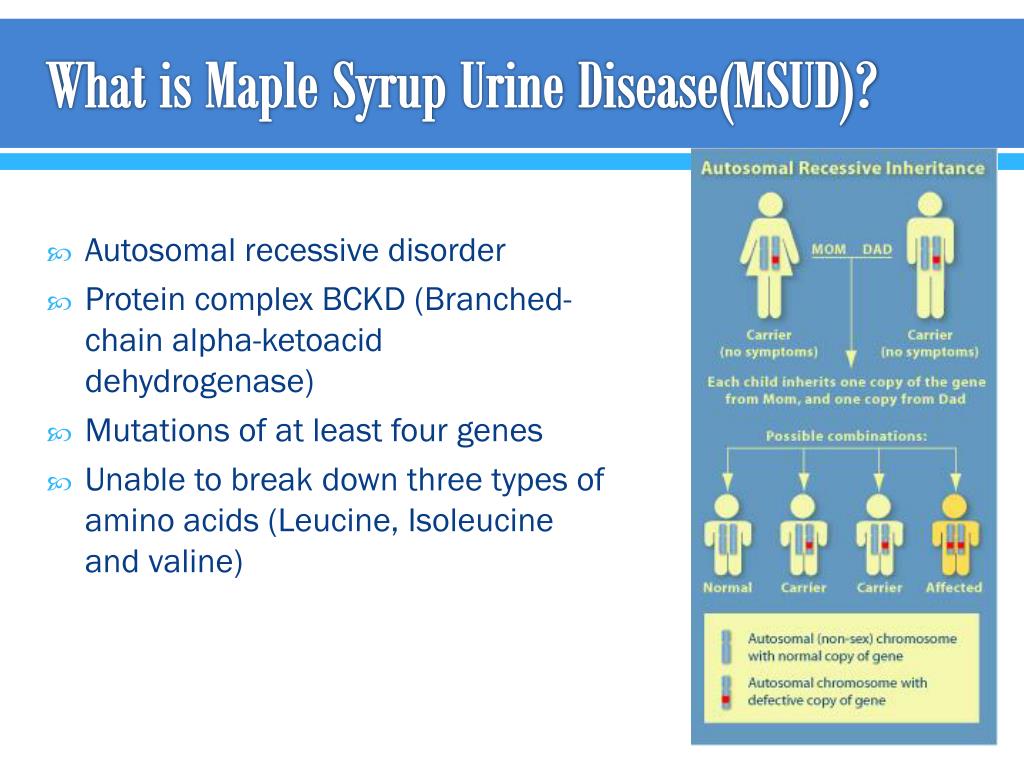
It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern and various different genes have been implicated 1. Maple syrup urine disease is due to mutations in any aspect of the mitochondrial branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex 8. Intermittent forms of the disease may present later (5 months to 2 years of age) and can be precipitated by concomitant infection or a high protein intake 8. characteristic odor of maple syrup in the urine or cerumen.It usually manifests itself within the first week of life with 8: Strauss KA et al (2020) Branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase deficiency (maple syrup urine disease): treatment, biomarkers, and outcomes. Orphanet (2014) Maple Syrup Urine Disease. OMIM (2018) Maple Syrup Urine Disease MSUD. Oglesbee D et al (2008) Second-tier test for quantification of alloisoleucine and branched-chain amino acids in dried blood spots to improve newborn screening for maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Menkes JH, Hurst PL, Craig JM (1954) A new syndrome: progressive familial infantile cerebral dysfunction associated with an unusual urinary substance. Up-to-dateĬhuang D (2001) Maple syrup urine disease (branched-chain ketoaciduria) The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease:1971–2005ĭancis J, Hutzler J, Levitz M (1960) Metabolism of the white blood cells in maple-syrup-urine disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 29:586–586īodamer O, Hahn S, Tepas E (2012) Overview of maple syrup urine disease. Bhattacharya K, Khalili V, Wiley V, Carpenter K, Wilcken B (2006) Newborn screening may fail to identify intermediate forms of maple syrup urine disease.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
